A tooth extraction is a dental procedure during which your tooth is completely removed from its socket. Sometimes, people refer to this as “pulling” a tooth.
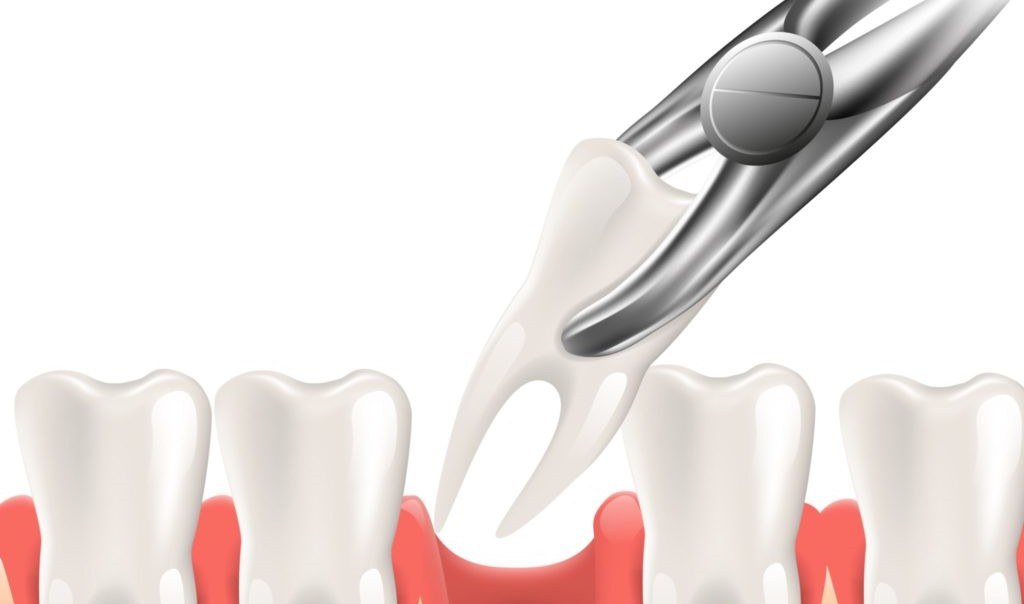
Healthcare providers prefer to save natural teeth whenever possible. But sometimes, other restorative methods — such as dental fillings or dental crowns — aren’t enough. If your tooth has been badly damaged past the point of repair, then removal may be necessary.
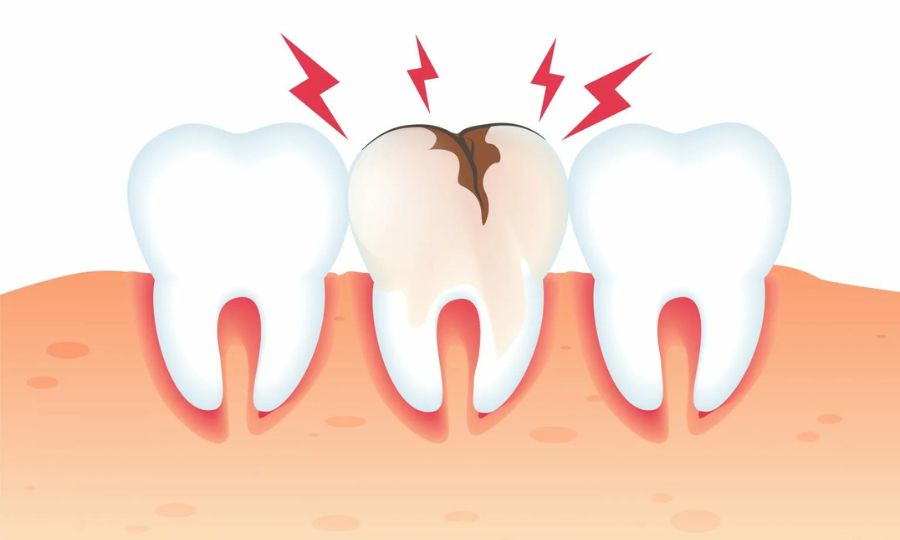
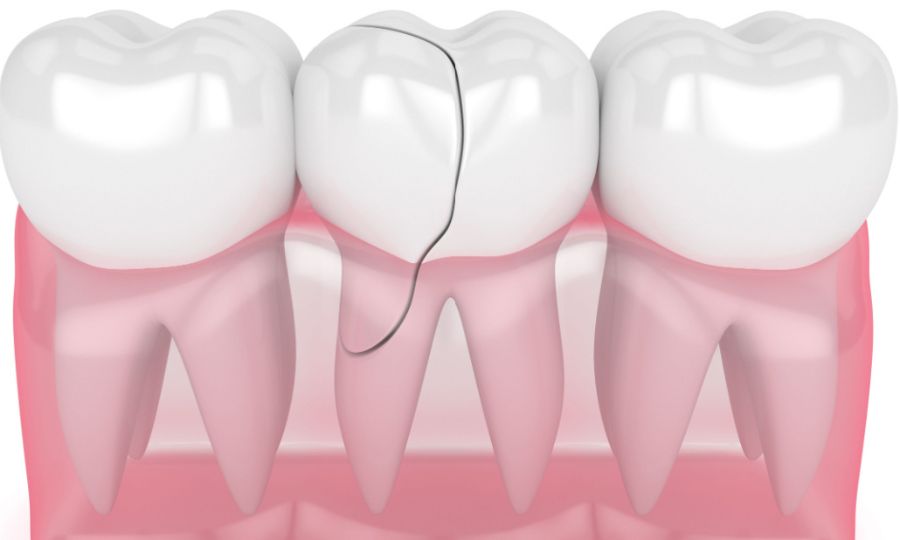
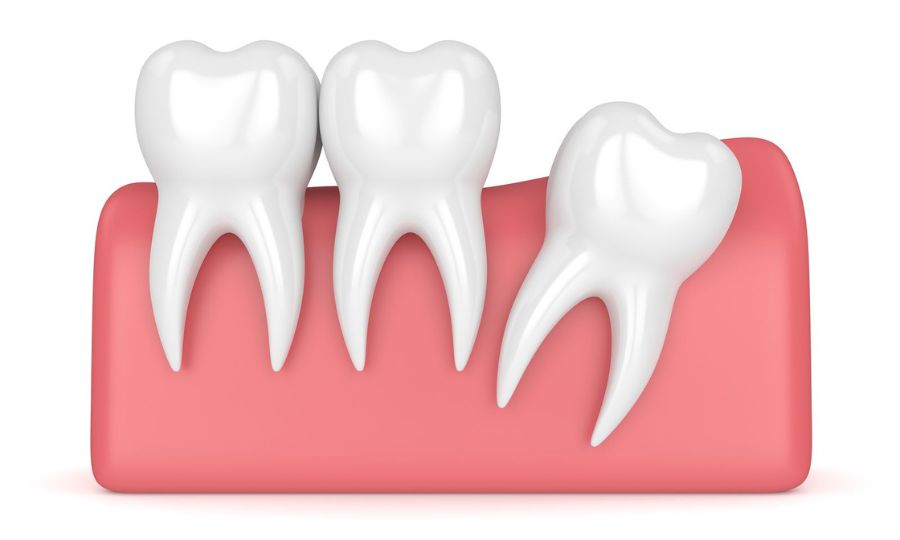
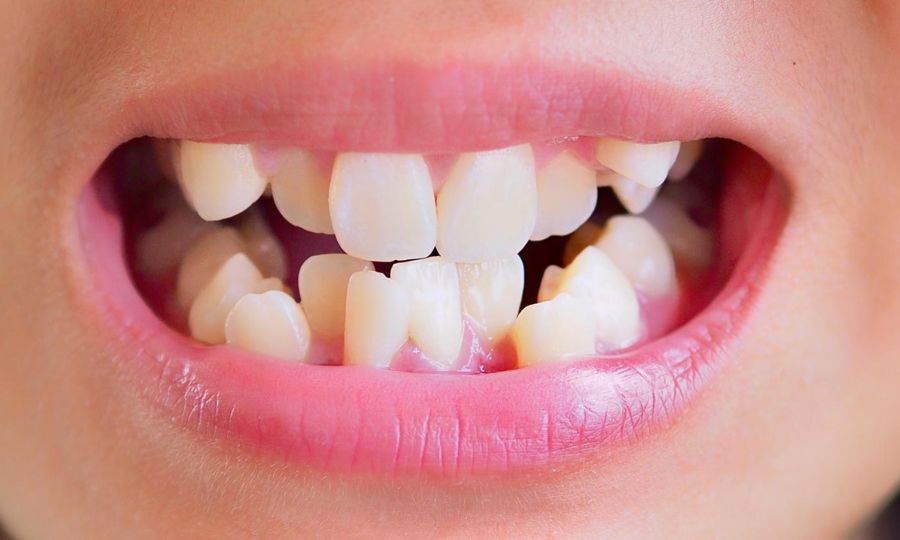

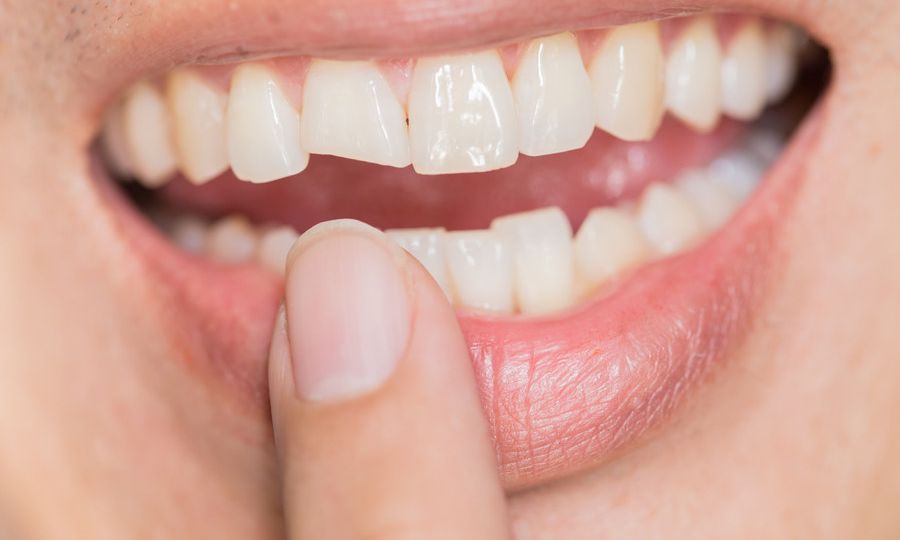

Your dentist will assess your affected tooth and surrounding gums. Your dentist will also take dental X-rays to check bone levels and determine the extent of damage. Be sure to tell your dentist about any medications, vitamins or supplements you’re taking. Once all information is gathered, treatment and sedation options will be discussed with you in detail.
First, local anaesthesia is given to numb your affected tooth and surrounding gum tissue. Using specialized dental instruments, your dentist will gently loosen your tooth and carefully lift it from its socket. Sometimes, your dentist might need to make incisions in your gums to access your tooth — especially if your tooth is badly decayed or has broken off at the gum line. Once your tooth is removed, the socket is cleaned and disinfected. In some cases, your dentist may also place a dental bone graft, which helps prevent bone loss in your jaw. Finally, stitches may be placed to help promote healing.
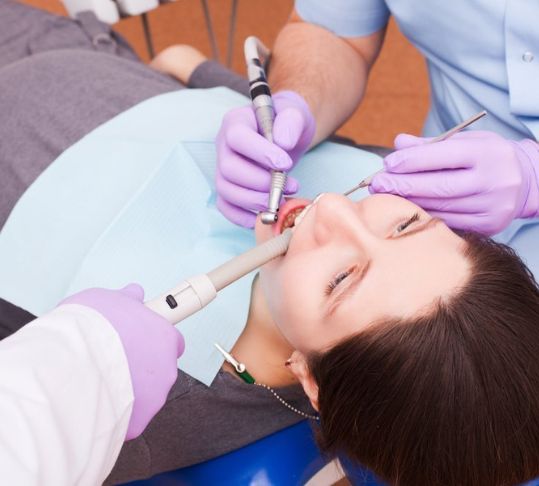

When the procedure is complete, your dentist will place a piece of gauze over the extraction site and ask you to close with firm, steady pressure. This helps slow bleeding so a blood clot can form. (Clotting is a normal aspect of recovery. It promotes healing and reduces the risk of dry sockets.) You’ll take the gauze out once the bleeding has slowed enough. You may continue to have light bleeding throughout the first 24 hours.